Venous Insufficiency Shoes - A Guide by Pedors Shoes
What is Venous Insufficiency?
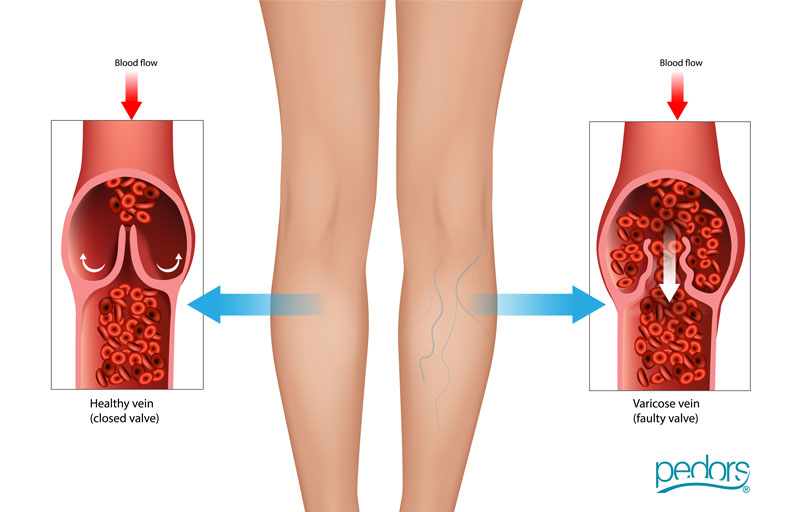
Venous insufficiency is a medical condition that occurs when the veins in the legs have difficulty returning blood from the legs to the heart. The veins in the legs contain one-way valves that help blood flow upward against gravity. In cases of venous insufficiency, these valves are damaged or weakened, leading to poor circulation and blood pooling in the lower extremities.

By Stephen O'Hare, President and Co-Founder, Pedors Shoes
For over 25 years Pedors Shoes has designed and manufactured shoes for problem feet. Our goal is to get our customers back on their feet again with affordable, quality footwear that addresses their specific needs. We’re here to help. Your footwear problems are our challenges.

The primary cause of Venous Insufficiency is often Chronic Venous Hypertension
Chronic Venous Hypertension is an increased pressure in the veins of the legs. This increased pressure can result from various factors, including:
Valve Dysfunction
The valves in the veins may become damaged or weakened, allowing blood to flow backward and pool in the veins.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Blood clots in the deep veins of the legs can damage valves and lead to venous insufficiency.
Varicose Veins
Enlarged and twisted veins near the surface of the skin (varicose veins) can contribute to venous insufficiency.
Prolonged Standing or Sitting
Jobs or lifestyles that involve long periods of standing or sitting can contribute to venous insufficiency.
Obesity
Excess body weight puts additional pressure on the veins in the legs.
Pregnancy
Changes in blood volume and hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy can affect vein function.
Symptoms of Venous Insufficiency may include:
Swelling
Swelling in the legs and ankles (edema).
Aching
Aching or throbbing pain in the legs.
Heaviness
Heaviness or fatigue in the legs, especially after prolonged standing.
Itching
Itching or tingling.
Skin changes
Skin changes such as discoloration or the development of ulcers.
Diagnosis of Venous Insufficiency
Diagnosis of venous insufficiency typically involves a physical examination and may include imaging tests such as ultrasound to assess blood flow in the veins.
Management and treatment of venous insufficiency may include:
Compression Therapy
Wearing compression stockings helps improve blood flow by providing external support to the veins.
Elevating the Legs
Keeping the legs elevated when possible helps reduce swelling.
Physical Activity
Regular exercise, especially activities that involve leg movement, promotes healthy blood circulation.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the pressure on the veins.
Medications
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to improve vein function and reduce symptoms.
For severe cases or complications, medical procedures such as vein stripping, laser or radiofrequency ablation, or sclerotherapy may be considered. It's important for individuals experiencing symptoms of venous insufficiency to seek medical evaluation for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
What are the risks if venous insufficiency is left untreated?
If venous insufficiency is left untreated, it can lead to various complications and worsening symptoms over time. The condition occurs when the veins have difficulty returning blood from the legs to the heart, causing blood to pool in the lower extremities. Here are some potential risks and complications associated with untreated venous insufficiency:
Varicose Veins
Persistent venous insufficiency can contribute to the development or worsening of varicose veins. These are enlarged, twisted veins near the surface of the skin that can cause discomfort and cosmetic concerns.
Venous Ulcers
Venous ulcers are open sores that develop on the skin, usually around the ankles. They result from long-term fluid buildup and increased pressure in the veins. Venous ulcers can be painful, slow to heal, and prone to infection.
Skin Changes
Chronic venous insufficiency can lead to skin changes such as hyperpigmentation (darkening of the skin), eczema, and lipodermatosclerosis (thickening and hardening of the skin). These changes may be irreversible if the underlying venous issues persist.
Cellulitis
Persistent swelling and compromised skin integrity increase the risk of cellulitis, a bacterial skin infection. Cellulitis can cause redness, swelling, and pain in the affected area and may require antibiotic treatment.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
In some cases, untreated venous insufficiency may contribute to the formation of blood clots in the deep veins (deep vein thrombosis). DVT poses a risk of serious complications if the clot travels to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism.
Chronic Venous Hypertension
Long-term venous insufficiency can lead to chronic venous hypertension, where elevated pressure in the veins affects the surrounding tissues. This can result in chronic pain, swelling, and skin changes.
Decreased Quality of Life
The symptoms of venous insufficiency, such as pain, swelling, and discomfort, can significantly impact an individual's quality of life. Untreated venous insufficiency may limit mobility and hinder daily activities.
Impaired Wound Healing
Venous insufficiency can impair the normal healing process, making wounds, cuts, or ulcers slower to heal. This increases the risk of infections and complications.
It's important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have venous insufficiency or are experiencing symptoms such as leg swelling, pain, or changes in skin appearance. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help manage symptoms, prevent complications, and improve overall vascular health. Treatment options may include lifestyle modifications, compression therapy, medications, and, in some cases, minimally invasive procedures to address underlying vein issues. Consulting with a healthcare professional, such as a vascular specialist or phlebologist, is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
Who are the medical professionals that treat for venous insufficency in legs and feet?
Several medical professionals can be involved in the diagnosis and treatment of venous insufficiency in the legs and feet. The specific healthcare provider you consult may depend on the severity of your condition and any associated symptoms. Here are some medical professionals who may be involved in the care of venous insufficiency:
Vascular Surgeon
Vascular surgeons are specialists who focus on the diagnosis and treatment of disorders affecting the blood vessels, including veins. They may perform procedures to address venous insufficiency, such as endovenous laser treatment or sclerotherapy.
For more information on vascular health visit https://vascular.org/
Phlebologist
A phlebologist is a medical professional who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of vein disorders. They may have a background in vascular medicine, dermatology, or general medicine.
For more information visit American Vein and Lymphatic Society.
Interventional Radiologist
Interventional radiologists use imaging techniques, such as ultrasound, to guide minimally invasive procedures for treating venous insufficiency. They may perform interventions like venous ablation or angioplasty.
To find a radiologist doctor near you here
Vascular Medicine Specialist
Vascular medicine specialists focus on the medical management of vascular conditions, including venous insufficiency. They may prescribe medications and recommend lifestyle changes to manage symptoms.
You can find a vascular specialist near you here
Dermatologist
Dermatologists may be involved in the care of venous insufficiency, especially when skin changes, such as discoloration or ulcers, are present. They can help manage skin-related issues associated with venous insufficiency.
For more information visit https://www.aad.org/
Cardiologist
In some cases, cardiologists may be consulted, particularly if there are concerns about the impact of venous insufficiency on the cardiovascular system.
Visit https://www.heart.org/ for more information.
General Practitioner or Family Medicine Physician:
Your primary care physician may be the first point of contact for evaluating symptoms of venous insufficiency. They can provide an initial assessment, make referrals to specialists, and coordinate your overall care.
https://familydoctor.org/
Podiatrist (Foot and Ankle Specialist):
Podiatrists specialize in conditions affecting the feet and ankles. If venous insufficiency is causing foot-related symptoms, a podiatrist can assess your condition, provide guidance on foot care, and recommend appropriate interventions.
For more information on Podiatry visit https://www.apma.org/
The specific healthcare professional you see may depend on your symptoms, the extent of your condition, and any underlying health issues. Often, a team-based approach involving multiple specialists may be employed to provide comprehensive care for venous insufficiency. If you suspect you have venous insufficiency or are experiencing symptoms such as leg swelling, pain, or skin changes, it's important to seek medical attention for a proper diagnosis and appropriate management.
What are the design features to look for in shoes for venous insufficiency?
Choosing the right footwear can be important for individuals with venous insufficiency, as supportive shoes can help promote proper circulation and alleviate some of the symptoms associated with this condition. Here are design features to look for in shoes for venous insufficiency:
Compression
Consider shoes with compression features or the ability to accommodate compression stockings. Compression can help improve blood flow in the legs.
Arch Support
Look for shoes with good arch support to promote proper foot alignment and reduce strain on the lower extremities.
Cushioning
Adequate cushioning in the insole and midsole can provide shock absorption and reduce impact on the feet, which can be beneficial for individuals with venous insufficiency.
Wide Toe Box
Shoes with a wide and roomy toe box allow for proper toe alignment and reduce pressure on the front of the foot. This can be particularly helpful for individuals with conditions like bunions or hammertoes.
Low Heel
A low or flat heel is preferable, as it reduces strain on the calves and promotes better blood circulation. High heels can exacerbate venous insufficiency symptoms.
Lightweight Construction
Lightweight shoes can help reduce fatigue and make walking more comfortable for individuals with venous insufficiency.
Adjustable Closures
Shoes with adjustable closures, such as Velcro straps or laces, allow for a customized and secure fit. This is especially important for accommodating any changes in foot swelling.
Breathable Materials
Shoes made from breathable materials, such as mesh or leather, can help maintain a comfortable temperature and reduce the risk of moisture-related skin issues.
Flat Seams and Soft Interior
Look for shoes with flat seams and a soft interior to minimize friction and irritation, reducing the risk of skin problems.
Removable Insoles
Shoes with removable insoles allow for customization with orthotic inserts or additional padding if needed.
Non-Slip Outsoles
Shoes with non-slip or slip-resistant outsoles provide stability and reduce the risk of slips and falls, which can be particularly important for individuals with compromised circulation.
Room for Swelling
Choose shoes that provide some extra room to accommodate potential foot swelling that may occur throughout the day.
Diabetic-Friendly Features
Some individuals with venous insufficiency may also have diabetes. Shoes with diabetic-friendly features, such as extra depth and a seamless interior, can be beneficial.
It's important for individuals with venous insufficiency to consult with healthcare professionals, such as a podiatrist or vascular specialist, for personalized advice on footwear. Additionally, getting professionally fitted for shoes can ensure the proper size and fit, contributing to overall foot health.

Conclusion on the Pedors Guide to Venous Insufficiency Shoes
If you have any questions please don't hesitate to email us at support@pedors.com or call 1-800-750-6729 if in the USA or +1 770 218 8282 if outside the USA.




